Microwave Communication - Section 1 (6)
- Home
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Electronics and Communication Engineering
- Microwave Communication - Section 1
Microwave Communication - Section 1
| 41. |
|
|||
Answer: Option A Explanation: An Impatt diode has n+ - p - i - p + structure and is used with reverse bias. It exhibits negative resistance and operates on the principle of avalanche breakdown. Impatt diode circuits are classified as broadly tunable circuit, low Q circuit and high Q circuit. The impedance of Impatt diode is a few ohms. The word Impatt stands for Impact Avalanche Transit Time diode. The features of Impatt diode oscillator are : frequency 1 to 300 GHz, Power output (0.5 W to 5 W for single diode circuit and upto 40 W for combination of several diodes), efficiency about 20%. Its applications include police radar systems, low power microwave transmitter etc. Avalanche diode can also be operated in large signal high efficiency mode called Trapped Avalanche Transit Time mode. The Trapatt oscillations depend on the delay in the current caused by avalanche process. The avalanche delay makes it possible to increase the diode voltage well above the breakdown voltage. Therefore a very rapid multiplication of charge carriers occurs. A Trapatt diode is also a negative resistance device. The features of Trapatt diode oscillator are : Frequency 3 to 50 GHz, Power output 1-3 W, efficiency about 25%. Its applications are low power doppler radar, microwave beacon landing system etc. |
| 42. |
|
|||||||
Answer: Option D Explanation: In a travelling wave both x and t increase simultaneously so that a constant phase point moves in the direction of positive (or negative) x. |
| 43. |
|
|||||||
Answer: Option A Explanation: In a klystron the resonant structure limits the bandwidth. A TWT is a broadband device. Its main components are electron gun (to produce the electron beam) and a structure supporting the slow electromagnetic wave. The velocity of wave propagation along the helix structure is less than velocity of light. The beam and wave travel along the structure at the same speed. Thus interaction occurs between beam and wave and the beam delivers energy to the RF wave. Therefore the signal gets strengthened and amplified output is delivered at the other end of tube. The main features of TWT are : 1. Frequency range - 0.5 GHz to 90 GHz 2. Power output - 5 mW at low frequencies(less than 20 GHz) 250 kW (continuous wave) at 3 GHz 10 MW (pulsed) at 3 GHz 3. Efficiency - about 5 to 20% 4. Noise - about 5 dB for low power TWT 25 dB for high power TWT TWT is used as RF amplifier in broadband microwave receivers, repeater amplifier in broad band communication systems, communication satellites etc. |
| 44. | Assertion (A): TWT uses a focussing mechanism to prevent the electron beam from spreading. Reason (R): In a TWT the electron beam has to travel a much longer distance than in klystron. |
|||||||
Answer: Option A Explanation: n a klystron the resonant structure limits the bandwidth. A TWT is a broadband device. Its main components are electron gun (to produce the electron beam) and a structure supporting the slow electromagnetic wave. The velocity of wave propagation along the helix structure is less than velocity of light. The beam and wave travel along the structure at the same speed. Thus interaction occurs between beam and wave and the beam delivers energy to the RF wave. Therefore the signal gets strengthened and amplified output is delivered at the other end of tube. The main features of TWT are : 1. Frequency range - 0.5 GHz to 90 GHz 2. Power output - 5 mW at low frequencies(less than 20 GHz) 250 kW (continuous wave) at 3 GHz 10 MW (pulsed) at 3 GHz 3. Efficiency - about 5 to 20% 4. Noise - about 5 dB for low power TWT 25 dB for high power TWT TWT is used as RF amplifier in broadband microwave receivers, repeater amplifier in broad band communication systems, communication satellites etc. |
| 45. |
|
|||||||
Answer: Option D Explanation:
|
| 46. |
|
|||||||
Answer: Option B Explanation: Some applications require dual polarization capability. Circular waveguide has this capability. These analysis uses cylindrical coordinates. In circular waveguide TE11 mode has the lowest cut off frequency and is the dominant mode. If D is diameter of waveguide λc = 1.706 D for TE11 mode λc = 1.029 D for TE21 mode λc = 0.82 D for TE01 mode λc = 1.306 D for TM01 mode. |
| 47. |
|
|||||||
Answer: Option A Explanation: A Klystron is a vacuum tube used for generation/amplification of microwaves. An electron beam is produced by oxide coated indirectly heated cathode and is focussed and accelerated by focussing electrode. This beam is transmitted through a glass tube. The input cavity where the beam enters the glass tube is called buncher. As electrons move ahead they see an accelerating field for half cycle and retarding field for the other half cycle. Therefore, some electrons are accelerated and some are retarded. This process is called velocity modulation. The velocity modulation causes bunching of electrons. This bunching effect converts velocity modulation into density modulation of beam. The input is fed at buncher cavity and output is taken at catcher cavity. In a two cavity klystron only buncher and catcher cavity are used. In multi cavity klystron one or more intermediate cavities are also used. The features of a multicavity klystron are : 1. Frequency range - 0.25 GHz to 100 GHz 2. Power output - 10 kW to several hundred kW 3. Power gain - 60 dB (nominal value) 4. Efficiency - about 40%. A multicavity klystron is used in UHF TV transmitters, Radar transmitter and satellite communication. |
| 48. |
|
|||||||
Answer: Option D Explanation: A pure reactance does not absorb any power. Therefore VSWR is infinite because |rv| = 1. |

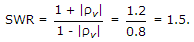 " src="https://indbix.in/uploads/2022/02/pic_1644070011.png" />
" src="https://indbix.in/uploads/2022/02/pic_1644070011.png" />